Binary Search Tree is one of the most commonly asked Data Structures in technical interviews. In this article, we will learn about what a binary search tree is and how to perform insertion into a node into a BST.
What is a Binary Search Tree?
A binary search tree is a node-based data structure similar to a Linked List. Where each node either has a null value or holds a reference to another node in the tree which is called a child node.
Rules of Binary Search Tree
For a Tree data structure to be characterized as a BST it must meet all the rules of a tree data structure along with the following rules:
Each node in a BST should have at most two children.
The left subtree of a node can only contain nodes with keys lesser than its relative parent node's keys.
The right subtree of a node can only contain nodes with keys greater than its relative parent node's keys.
Meeting all the above rules, a basic binary search tree looks something like this:
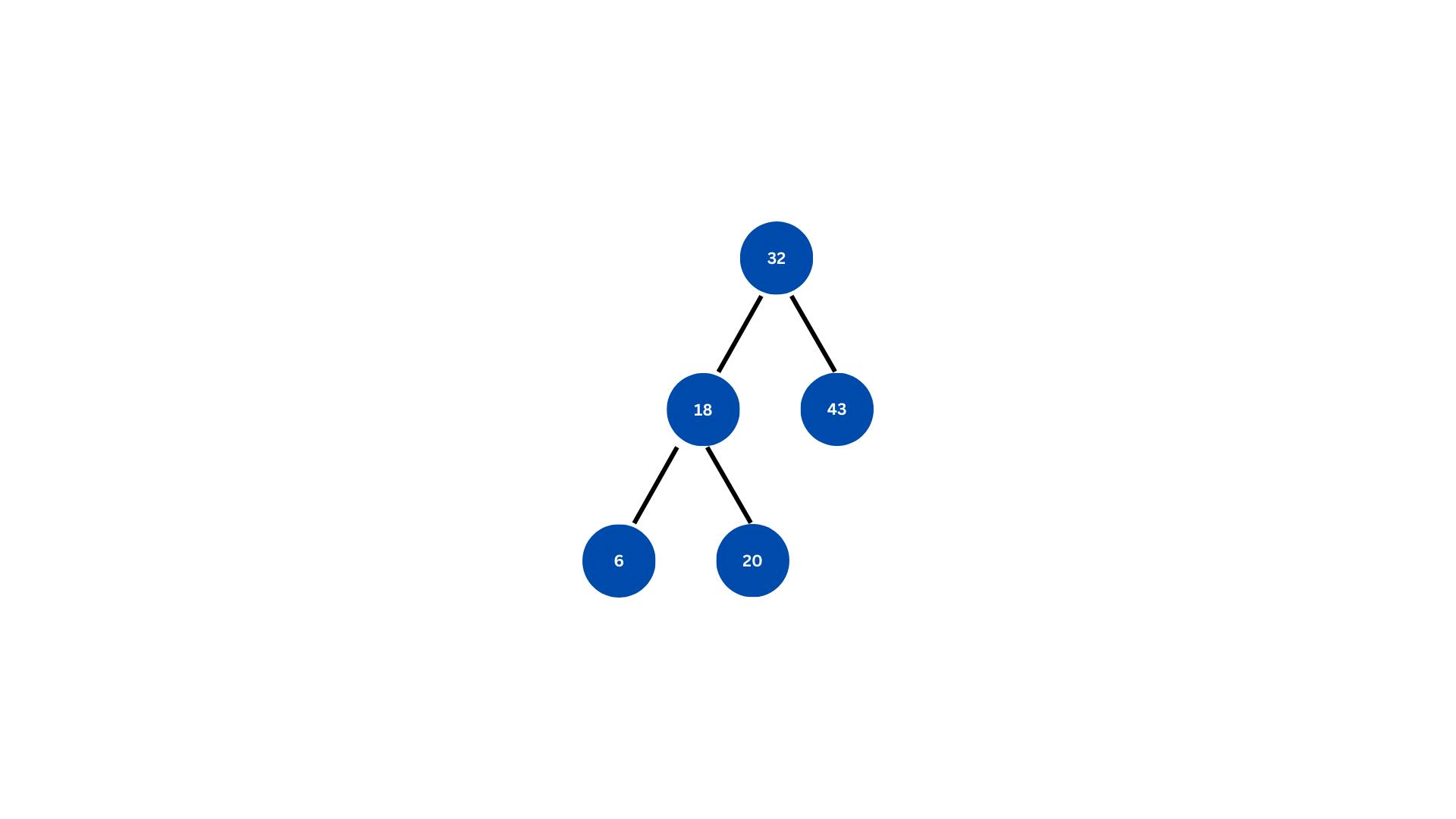
Here, 32 is our root node which has two child nodes that are sorted as per the rules of a BST.
Creating a Binary Search Tree in Javascript
Now that we know what is a BST and what are its rules. Let's now jump to the coding part and create a Binary Search Tree in Javascript.
The first thing that we need to do is define a Node class, which will represent each individual node of a BST.
class Node {
constructor(val){
this.value = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
Here, each node in our binary search tree will have 3 properties:
value: the value of the node.left: this will have reference to the left subtree of the node.right: this will have reference to the right subtree of the node.
Next, we will create our BinarySearchTree class as follows:
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(){
this.root = null;
}
}
BinarySearchTree class will have only one property root which will be the root of our BST.
We now have created our BinarySearchTree class, let's see how we can insert nodes to our empty BST.
Insertion in a Binary Search Tree
To insert new nodes to a BST we can either use the iterative approach or the recursive approach. In this article, I am using the iterative approach just for the sake of simplicity.
So let's first create the insert method inside our BinarySearchTree class, our insertion logic will go inside this method.
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(){
this.root = null;
}
insert(val){
// Insertion logic will go here...
}
}
This method will take one parameter val which will be the value that we want to insert into our BST.
Now, let's write our insert logic. The very first condition that we need to check is, if we don't have a root present in our BST then the inserted node will become the root.
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(){
this.root = null;
}
insert(val){
// Create a new node using the Node class that we created
const newNode = new Node(val);
if(this.root === null) {
// Save the newNode as the root
this.root = newNode;
// Return the entire BST and exit the function
return this;
}
}
}
We have our first condition covered. Now we can insert nodes into our empty BST and that node should become the root of the BST.
const BST = new BinarySearchTree;
BST.insert(32)
The above code should add a new root to the BST if it is empty.
If it already has a root, we need to write a condition to check if the val that we are inserting is less than the root value.
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(val) {
const newNode = new Node(val);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
return this;
}
// Create a temporary variable which will keep track of the current node that we are at, by default it will equal to this.root
let current = this.root;
// Traverse over the tree
while (true) {
// If the new value is less than the current value
if (val < current.value) {
// Check if there is no left node
if (current.left === null) {
// Save the newNode as the new left node
current.left = newNode;
// Return the entire BST & terminate the loop
return this;
} else {
// Else if there is a left node
// Move current to current.left and repeat the entire steps again
current = current.left;
}
}
}
}
}
Then, we will write a condition to check if the new val is greater than the root value.
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(val) {
const newNode = new Node(val);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
return this;
}
let current = this.root;
while (true) {
if (val < current.value) {
if (current.left === null) {
current.left = newNode;
return this;
} else {
current = current.left;
}
} else if (val > current.value) {
// If val is greater than root.value
// Check if there is no node to the right of the root
if (current.right === null) {
// Save the newNode as the new right node
current.right = newNode;
// Return the entire BST & terminate the loop
return this;
} else {
// Else if there is a right node
// Move current to current.right and repeat the entire steps again
current = current.right;
}
}
}
}
}
One last thing that we need to check is the edge case that is, if we are trying to insert a duplicate value. There are lots of ways to handle this but in our case, we will return undefined if we try to insert a duplicate value to the binary search tree.
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(val) {
const newNode = new Node(val);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
return this;
}
let current = this.root;
while (true) {
// Base condition: If val is equal to current.value which means it is a duplicate value
if(val === current.value) return undefined;
if (val < current.value) {
if (current.left === null) {
current.left = newNode;
return this;
} else {
current = current.left;
}
} else if (val > current.value) {
if (current.right === null) {
current.right = newNode;
return this;
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
}
}
}
That's all the code that we need to perform insertion in a binary search tree.
Complete Code
This is the complete code for our BinarySearchTree example with insert method using Javascript:
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.value = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(val) {
const newNode = new Node(val);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
return this;
}
let current = this.root;
while (true) {
if(val === current.value) return undefined;
if (val < current.value) {
if (current.left === null) {
current.left = newNode;
return this;
} else {
current = current.left;
}
} else if (val > current.value) {
if (current.right === null) {
current.right = newNode;
return this;
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
}
}
}
So that's it for this article. I hope this article was able to teach you something.
Consider giving a thumbs up and follow me for more blogs. You can also connect with me on Twitter where I keep sharing regular content related to web development, Javascript, and other related stuff.